EAR -TRAUMATIC EAR PERFORATION Treatment
Traumatic ear perforation
Traumatic perforation of the tympanic membrane causes sudden severe pain sometimes followed by bleeding from the ear, hearing loss, and tinnitus. Hearing loss is more severe if the ossicular chain is disrupted or the inner ear is injured.
Signs and symptoms of a ruptured eardrum may include:
- Ear pain that may subside quickly.
- Mucuslike, pus-filled or bloody drainage from your ear.
- Hearing loss.
- Ringing in your ear (tinnitus)
- Spinning sensation (vertigo)
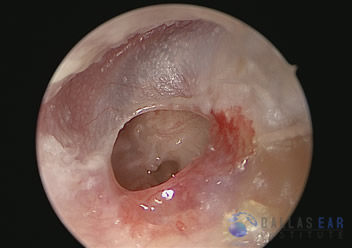
Simple traumatic tympanic membrane perforation (TTMP) remains the most common type of trauma – induced otologic dysfunction. 5Treatment of TTMP range from inactive watchful waiting, active intervention to surgical intervention. Otolaryngologists have however been advised to be reluctant in offering surgical intervention in cases of TTMP without significant symptoms as most patients will heal spontaneously within two months. Active interventions include topical application of substances like epidermal growth factor, enoxaparin, and ascorbic acid to stimulate epithelization for quick closure or to prevent formation of sclerotic plaques in the perforated membrane.
Surgical intervention are indicated in cases of complications like perilymph fistula, facial paralysis, severe vertigo, or profound sensorineural hearing loss. Such diagnosis should be made early and treatment offered promptly.Surgical treatment included exploration and tympanoplasties, closure of the perforation with stents in the form of simple patches, or as patches laden with substances in the form of silk fibroin membranes, or steri-strips patching. These technical surgeries require high expertise and necessary equipment which may not be readily available in the low socio-economic countries. In such less ideal situations, it will be necessary to characterize traumatic tympanic membrane (TM) perforation if optimal treatment is desirable. Our hospital is a relatively high volume trauma center and cases of injuries to the ears involving the tympanic membranes are readily seen. Characterizing such lesion will provide an impetus for better management of affected patients.
Traumatic Eardrum Perforation Treatment: What You Need to Know
The eardrum, also known as the tympanic membrane in technical terms, is essential for both sound transmission and inner ear protection. It can cause discomfort, hearing loss, and other symptoms when it is perforated. When it is perforated, it can cause pain, hearing loss, and other symptoms. Timely treatment is essential to promote healing and prevent long-term complications.
Signs of a Traumatic Eardrum Perforation
The severity of the injury can affect the symptoms of a traumatic eardrum perforation.
Common symptoms include:
- Sudden ear pain: The pain may subside after a while, but it can be intense initially.
- Drainage from the ear: You can see a pus-like or red discharge coming from the ear.
- Hearing loss: Eardrum damage can cause partial or total hearing loss.
- Tinnitus: Ringing in the ear, also known as tinnitus, is another symptom that may accompany a perforated eardrum.
- Vertigo: A spinning sensation or dizziness may occur if the inner ear is affected.
Treatment for Traumatic Eardrum Perforation
Most cases of traumatic eardrum perforation heal on their own within two months without the need for surgery. However, treatment depends on the severity of the injury and the associated symptoms. Here are some treatment options:
Watchful Waiting
In many cases, particularly when the symptoms are mild, the doctor may recommend a wait-and-watch approach. The perforated eardrum typically heals on its own within 6 to 8 weeks. During this time, keeping the ear dry and avoiding further trauma to the eardrum is crucial.
Active Interventions
If the perforation is not healing as expected or if complications arise, an ear specialist may recommend more active treatments. This can include:
- Topical treatments: The application of certain substances like epidermal growth factor or ascorbic acid may stimulate healing and help the eardrum close faster.
- Antibiotics: In cases where there is infection, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent further complications.
Surgical Treatment
In rare cases, when there are severe complications such as perilymph fistula, facial paralysis, or significant hearing loss, surgery may be necessary. The surgical options include:
- Tympanoplasty: A procedure to repair the eardrum using grafts or synthetic materials.
- Eardrum patching: A minimally invasive approach to seal the perforation with special materials, such as silk fibroin membranes.
Consult an Ear Specialist in Nashik
If you suspect a traumatic eardrum perforation, it is essential to consult with an Ear Specialist in Nashik. An experienced ENT specialist can assess the severity of the injury, recommend appropriate treatment, and ensure that your ear heals properly. Don't ignore symptoms like persistent pain or hearing loss—seeking timely care can prevent further complications and help restore your hearing.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of a ruptured eardrum, make an appointment with a trusted Ear Specialist in Nashik to get the proper diagnosis and treatment.
